Redactor Redactor 2.x Custom formats in Redactor
With custom formatting options, you can add custom styles and formats to the standard Formatting dropdown. These can include inline styles, classes and also calls to internal API methods. Custom formatting is specified as a JSON array, and is added to the redactor.formattingAdd system (or context) setting.
A Basic Example
[{
"tag": "p",
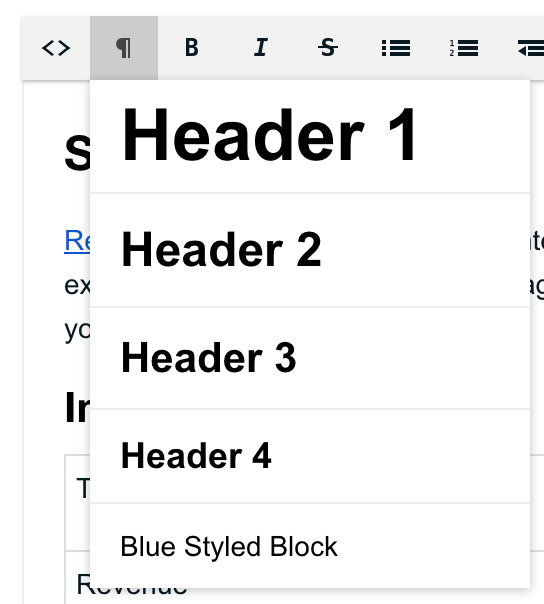
"title": "Blue Styled Block",
"class": "blue-styled"
}]
When this is added to the redactor.formattingAdd setting, it will add one new option to the formatting dropdown titled Blue Styled Block. When chosen it will add or update the p (paragraph) tag, with a class of blue-styled applied.
Note that Redactor will use the tag plus the class as a unique identifier for the formatting, so make sure that each option has a unique combination of tag and class.
To add more formatting options, just add more elements:
[{
"tag": "p",
"title": "Blue Styled Block",
"class": "blue-styled"
},{
"tag": "p",
"title": "Red Styled Block",
"class": "red-styled"
}]
Adding Styling to the Formatting Dropdown
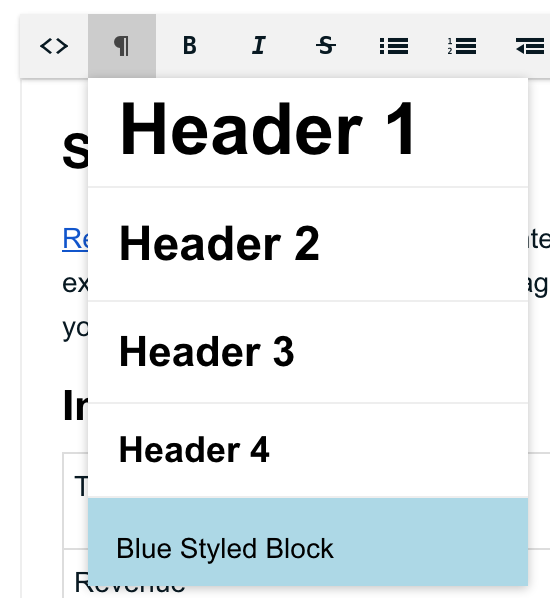
In the formatting dropdown, the newly added formatting option wont look very different just yet. This can be done in two different ways. The first one is to add an inline style to the formatting option, by adding the style attribute to your JSON.
[{
"tag": "p",
"title": "Blue Styled Block",
"class": "blue-styled",
"style": "padding: 1em; background: lightblue;"
}]
By adding a simple style attribute to the formatting definition, the style is immediately visible in the dropdown. This is a great help for end users to pick the formatting style they need, and of course you can also add font-related styles like a color or font-family.
The second option is to use a custom css file, targeting a class that is built up like this:
.redactor-dropdown .redactor-formatting-{tag}
.redactor-dropdown .redactor-formatting-{tag}-{class}
For example the CSS selector for our Blue Styled Block would be: .redactor-dropdown .redactor-formatting-p-blue-styled
Adding Styling to the Editor
The editor does not apply inline styles, so to make your editor look similar to what the user might expect from the front-end, you will need to create a custom CSS file. In this file, you would add a subset of the styles from you frontend CSS.
All CSS declarations need to be scoped to the .redactor-editor class. If you don’t properly scope the CSS, you will find it starts affecting the rest of the manager in a way that you probably didn’t want to.
The CSS file can be anywhere, for example in /assets/template/redactor.css to keep it along your other assets. Inside the css file, you target html nodes within .redactor-editor just like you would target them in the front-end. For the simple example above, that might look like the following.
.redactor-editor p.blue-styled {
padding: 1em;
border: 1px solid blue;
background: lightblue;
}
Once you have a CSS file, you can go into the System Settings and add the link to it in the redactor.css setting. Just set the link like /assets/template/redactor.css and Redactor will add it to the page. With the CSS in place, we will start seeing results in the editor
As mentioned in the previous section, you can also use the custom CSS file for styling the dropdown. If you do that, you wont have to define the style in your JSON. If you’re already using it for the editor, adding it to the dropdown too is simple:
.redactor-dropdown .redactor-formatting-p-blue-styled,
.redactor-editor p.blue-styled {
padding: 1em;
border: 1px solid blue;
background: lightblue;
}
Available Attributes
We’ve already seen tag, title, class and style, but here’s the full list of what attributes you can use in the custom formats JSON.
-
tag: the HTML tag to apply the styles to. Primarily supports p, pre, blockquote and header; -
title: what the formatting option is called in the formatting dropdown; -
class: a class to apply to the HTML tag, useful for styling and stuff; -
style: a simple CSS style definition to apply to the formatting option in the dropdown; -
attr: can be used to apply an arbitrary attribute to a tag. Specify as an object with keys “name” and “value”. For example"attr":{"name": "title", "value": "Hello World!"}will addtitle="Hello World!"to the tag. -
data: similar toattr, except this can also set data attributes. Also specified as an object with keys name and value. For example"data":{"name":"data-separator", "value":"true"}will adddata-separator="true"to the tag. -
clear: when set to true, existing styles and classes will be removed from the tag before applying the styles of the specific formatting option. Example"clear": true. -
func: useful to trigger an internal API method, for exampleinline.removeFormatto remove all formatting.
More information is available in the Redactor.js formattingAdd documentation.